Briefly Explain the Difference Between Current Prices and Constant Prices
The key difference between current price and constant price is that GDP at current price is the GDP unadjusted for the effects of inflation and is at current market priceswhereas GDP at constant price is the GDP adjusted for the effects of inflation. Measurement always originally occurs at current prices.

Difference Between Current Price And Constant Price Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
Current prices make no adjustment for inflation.
. We say that it is used to convert GDP at current prices to GDP at constant prices ie removes the fefect of inflation. Current price depends on the supply and demand curveIf the supply is more and demand is less the current price will go down and reverse is equally true. Current prices are those indicated at a given moment in time and said to be in nominal value.
Use examples to answer the question. Intrinsic value is an estimate of the actual true value of a company regardless of market value. The key difference between current price and constant price is that GDP at current price is the GDP unadjusted for the effects of inflation and is at current market prices whereas GDP at constant price is the GDP adjusted for the effects of inflation.
Current Prices measures GDP inflationasset prices using the actual prices we notice in the economy. Current Prices And Constant Prices Economics Help. The GDP deflator is a broad index of price increases than the consumer price index CPI is the usual measure of inflation.
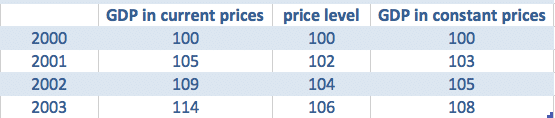
The increase in product or income is not due to increase in product or output but due to the rise in price level. From the above table it is found that national income at current prices is 29700 whereas the national income at constant prices is 14100. Red a Logo Company.
SelectedJun 26 2018by rubby. Two main differences between GDP at current prices and at constant prices are. The relationship between current price and constant price is that GDP constant price is derived from the GDP current price.
A year is chosen as the base year. National Income at Current Prices and Constant Prices Nominal NI and Real NI National income can be measured in terms of money in two ways a at current prices and b at constant pricesa National income at current prices. It requires conversion of national income at current prices in terms of the prices of the year of reference called the base year.
This shows the UK real GDP GDP adjusted. Ii GDP at current prices may increase even if there is no flow of goods and service whereas GDP at. Briefly Explain the Difference Between Constant and Current Prices.
The terms constant euros or constant francs and current euros or francs are used in the same way. The relationship between current price and constant price is that GDP constant price is derived from the GDP current price. For example current price data shown for 1990 are based on 1990 prices for 2000 are based on 2000 prices and so on.
The Unit Product Cost of a Blender Is 24. National Income at Current PricesWhen national product is estimated on the basis of prices prevailing in the current year it is called national income at current prices or nominal national income. It can be used to calculate real changes in the level of GDP.
National income at constant prices National income at current pricesPrice index of current year x Price index of base year. National Income at Current Price National Income at Constant Price Current Price Index x 100. Using constant prices enables us to measure the actual change in output and not just an increase due to the effects of inflation.
Constant series show the data for each year in. It includes the prices of capital goods as well as consumer goods. Constant price will not depend on the variables of supply and demand.
Briefly explain tg difference between constant and current prices in the BOP Get the answers you need now. Other series in World Development Indicators WDI show data in constant or real terms. N1 at current price is more because the prices of current year are immensely high.
Explain the difference between measurement at current prices and constant prices respectively. If goods and services produced in a year are valued at current prices ie prices prevailing in that particular year we get national income at current. For example if price index for the current year is 150 and national income at current price is Rs 1 50000 then the national income at constant price will be.
Corrected for changes in prices in relation to a base line or reference datum. The actual level of the GDP is however not of prime importance. Constant prices are in real value ie.
Market value is the current value of a company as reflected by. To illustrate the point suppose national income at current prices for an economy is Rs 10000 crores. Constant prices are a way of measuring the real change in output.
I GDP at current prices are measured at current years prices whereas GDP at constant prices are measured at base years prices. For any subsequent year the output is measured using the price level of the base year. And the price index of the current year with respect to 1991 as the base year is 250.
49 rows Definition. This excludes any nominal change in output and enables a comparison of the actual goods and services produced. For example the GDP for 2018 is originally measured at 2018 prices.
The current prices are real and used nowadays to buy goods and services while the adjusted ones are modified in order to compare the GDP in economies. Constant prices adjust for the effects of inflation. SukhmaniA8547 sukhmaniA8547 03032019 Economy Secondary School answered Briefly explain tg difference between constant and current prices in the BOP 2.

Difference Between Current Price And Constant Price Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
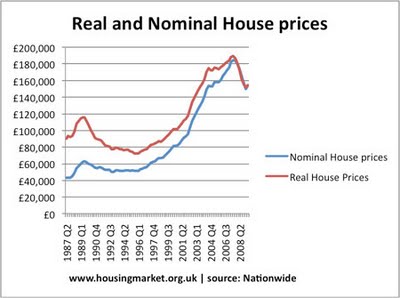
Current Prices And Constant Prices Economics Help

Current Prices And Constant Prices Economics Help
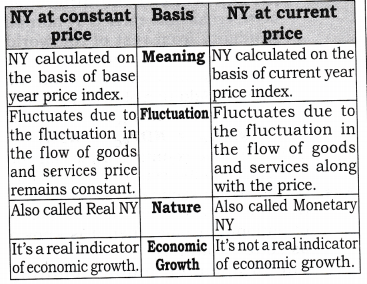
Ncert Solutions For Class 12 Macro Economics National Income And Related Aggregates Learn Cbse
No comments for "Briefly Explain the Difference Between Current Prices and Constant Prices"
Post a Comment